The Risks and Prevention of Cervical Cancer
Previously a major cause of death for women, cervical cancer is now mostly avoidable with the help of screening programs, immunization campaigns, and greater public awareness. Nonetheless, it still affects millions of people worldwide, underscoring the necessity of more information and easily accessible treatment. This article explores the main features of cervical cancer, educating readers and highlighting the value of taking preventative action.
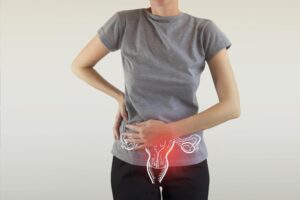
Cervical cancer:
What is curvical cancer ? Uncontrolled proliferation of abnormal cells in the cervix, the lower region of the uterus that connects to the vagina, is the cause of cervical cancer. The main offender is a chronic infection with specific strains of the sexually transmitted virus known as human papillomavirus (HPV). While the majority of HPV infections resolve on their own, some high-risk strains, such as HPV 16 and 18, can persist and, if ignored, cause cellular alterations that result in cancer.
Influencing elements:
Cervical cancer can arise due to various reasons, although HPV infection is the predominant cause. These variables include:
- Age at which first sexual contact occurred: Early initiation of sexual intercourse gives the virus more chance to persist.
- Having several sexual partners: The risk is increased by increased exposure to various HPV strains.
- Weakened immune system: The body’s capacity to combat HPV infection may be compromised by illnesses such as HIV/AIDS.
- Smoking: Smoking impairs immunity and destroys cervical cells.
- Extended usage of oral contraceptives: Although the risk is negligible, continued use may marginally raise susceptibility.
Early Warning Signs:
When cervical cancer is first developing, it frequently advances silently. Nonetheless, the following are a few possible red flags to watch out for:
- Unusual vaginal bleeding during or after menopause, or bleeding more heavily than usual.
- Pelvic pain, particularly during sex,.
- Discreet, malodorous vaginal discharge.
Diagnostic Tests:
To ensure early detection, routine HPV and Pap tests are essential. A Pap test looks for abnormal cells in the cervical cavity, but an HPV test detects the virus itself. If abnormalities are found, biopsies and colposcopy may also be used for additional assessment.
Immunization for Prevention: The best way to prevent cervical cancer is to get vaccinated against HPV, which is available for both boys and girls. When taken before sexual activity, it guards against high-risk HPV infection and dramatically lowers the chance of acquiring cervical cancer in the future.
Preventive actions:
In addition to vaccination, condom-using during safe sex and reducing the number of sexual partners can help lower HPV exposure. Furthermore, as advised by medical professionals, routine HPV and Pap tests are critical for early identification and treatment.
Also Read about Poonam Pandey Death from cervical cancer
Options for Treatment:
Cervical cancer treatment options are contingent upon a number of circumstances, such as the cancer’s stage and kind and the patient’s general condition. Typical methods include the following:
- Surgery: Cervical excision and surrounding tissue removal via hysterectomy or conization.
- Radiation therapy: destroying cancer cells with high-energy radiation.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs are used to kill cancer cells all over the body.
Global Disparities:
Regrettably, there are still disparities in the availability of the HPV vaccine, screening programs, and efficient treatment throughout the world. The burden of cervical cancer is disproportionately higher in low- and middle-income nations because of a lack of awareness and resources for healthcare. In order to address this global health crisis, expanding access to these essential tools is imperative.
Research is still being done.
done to create vaccinations that are even more effective, enhance screening methods, and investigate novel treatment approaches for cervical cancer. Furthermore, worldwide success against this preventable disease depends on studies addressing healthcare inequities and increasing awareness in marginalized areas.
Together, we can make a lasting impact and ensure that cervical cancer awareness is a priority 365 days a year! 🌈
#CervicalCancerAwareness #cervicalcancer #cervivor pic.twitter.com/j5rdZznWa9— CureCervicalCancer (@CCCorganization) January 31, 2024
Remember:
People may drastically lower their risk of acquiring cervical cancer by being aware of the risk factors, taking preventative steps, and getting frequent exams. Seek individualized advice and assistance from your healthcare professional if you have any concerns. Working together, we can make cervical cancer preventive for everyone in the future.
2 thoughts on “Empowering Women: Understanding the Risks and Prevention of Cervical Cancer”